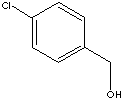
| 4-CHLOROBENZYL ALCOHOL | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 873-76-7 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 212-852-2 | |
| FORMULA | ClC6H4CH2OH | |
| MOL WT. | 142.58 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | p-Chlorobenzyl alcohol; (4-Chlorophenyl) methanol; | |
| 4-chlorobenzenemethanol; 4-Chlorbenzylalkohol; Alcohol 4-clorobencilico; Alcool 4-chlorobenzylique; | ||
| DERIVATION | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | 70 - 72 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 234 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.2 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 2.5 (g/l at 20 C) | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 2; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | 70 C | |
| STABILITY | stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
| Benzyl is the
prefix describing the presence of the redical "C6H5CH2-". An simple example
is benzyl alcohol, C6H5CH2OH.
Benzyl alcohol, also called phenylmethanol or
phenylcarbinol, is a clear, colorless
liquid with a mild pleasant aromatic odor; melting at 15 C and
Boiling at 205 C. It is a primary alcohol with arene group. It is soluble in
water and readily soluble in alcohol and ether. Benzyl alcohol is prepared by
the hydrolysis of benzyl chloride in the presence of soda ash.
Benzyl alcohol has properties of
strong polarity and limited water solubility. It features also good
solvency, low toxicity and low vapor pressure. It is used as a general
solvent for inks, paints, lacquers, epoxy resin coatings, and as a degreasing
agent in cleaning as well as for chemical reaction process. It reacts with acids
(acetic, benzoic, and sebacic acids, and etc) to form numerous esters, salts and
other compounds, thus is used widely as a valued intermediate in industrial
field as well as in making soap, perfume, and flavors. This compound is used
as a dyeing assistant for filament nylons.
Its applications include many pharmaceutical
preparations and bacteriostatic compounds. It was used for antipruritic activity
to relieve itching. Carbinol is a primary alcohol with general formula
RCH2OH. In carbinol
nomenclature system, the term of carbinol is methanol itself and other groups
are considered to have replaced one of the methanol hydrogen atoms to describe
larger alcohols as derivatives of carbinol. This nomenclature system is
particularly useful when the groups attached to the methanol carbon are large,
aromatic, and cyclo groups. Benzyl alcohol is
called phenylcarbinol or
benzenecarbinol while benzyl carbinol is phenylethyl alcohol.
Alcohols are widely used as solvents, fuels and chemical raw materials. Generally, hydroxyl group compounds are polar, which trends to promote solubility in water. But the carbon chain resist to solubility in water. Short chain alcohols (methanol, ethanol, and propanol) in which the hydroxyl group predominates are miscible in water. Butanol is moderately soluble because of the balance between the two opposing solubility trends. Higher alcohols are practically insoluble in water because of the hydrocarbon chain's trend is stronger. Alcohols are "protic" solvents. Protic refers to a hydrogen atom attached to an electronegative atom, oxygen. Polar protic solvents are compounds that can be represented by the general formula ROH of which water (H2O), methanol (CH3OH) and acetic acid (CH3COOH) are examples. Alcohols are very weak acids as they lose lose H+ in the hydroxyl group. Alcohols undergoes dehydration reaction which means the elimination of water molecule replaced by a pi bond between two adjacent carbon atoms to form alkenes under heating in the presence of strong acids like hydrocloric acid or phosphoric acid. Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes and ketones respectively. Carboxylic acids are obtained from oxidation of aldehydes. Oxidation in organic chemistry can be considered to be the loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen and reduction to gain hydrogen or loss of oxygen. Tertiary alcohols do not react to give oxidation products as they have no H attached to the alcohol carbon. Alcohols undergoes important reactions called nucleophilic substitution in which an electron donor replaces a leaving group, generally conjugate bases of strong acids, as a covalent substitute of some atom. One of important reaction of alcohol is condensation. Ethers are formed by the condensation of two alcohols by heating with sulfuric acid; the reaction is one of dehydration. Almost infinite esters are formed through condensation reaction called esterification between carboxylic acid and alcohol, which produces water. Alcohols are important solvents and chemical raw materials. Benzyl alcohol, or a derivative thereof, is used as a:
|
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | |
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|
|
TRANSPORTATION |
||
| PACKING | 240kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: , Safety Phrases: 24/25-28A-37-45 | ||